Choke for a DRL 250 lamp. Ultraviolet - we get it at home quickly and for pennies
Topic: connection diagram, characteristics, device, operation of the DRL lamp.
DRL lamp(Arc Mercury Lamp) - high pressure arc mercury phosphor lamp. This is one of the types of electric lamps that is widely used for general lighting of large areas such as factory floors, streets, playgrounds, etc. (where there are no special requirements for the color rendering of lamps, but high luminous efficiency is required from them). DRL lamps have a power of 50 - 2000 W and are initially designed to operate in electrical networks alternating current with supply voltage 220 V. (frequency 50 Hz.). To operate the lamp, a starting and regulating device in the form of an inductive choke is required.
Now, regarding the device of the DRL lamp. A mercury arc lamp (MALV) consists of three main functional parts: a base, a quartz burner and a glass bulb.
Base is designed to receive electricity from the network by connecting the lamp contacts (one of which is threaded and the other is point-type) with the socket contacts, after which alternating electricity is transferred directly to the electrodes of the DRL lamp burner itself (electric mercury arc lamp).
Quartz burner is the main functional part of the DRL lamp. It is a quartz flask with 2 electrodes on each side. Two of them are basic and two are additional. The burner space is filled with inert gas “argon” (to isolate heat exchange between the burner and the medium) and a drop of mercury.
Glass flask - this is the outer part of the lamp. A quartz burner is placed inside it, to which conductors are connected from the contact base. Air is pumped out of the flask and nitrogen is pumped into it. And one more important element that is located in the glass flask is 2 limiting resistances (connected to additional electrodes). The outer glass bulb is coated with phosphor on the inside.
The first versions of DRL lamps had only two electrodes, which required an additional triggering device (through a high-voltage pulsed breakdown of the gas gap of a quartz burner) to ignite the DRL lamp. This type of lamp was discontinued and replaced with a four-electrode analogue, which only requires a choke to operate.
Main characteristics of DRL lamps:

DRL lamp operation : mains voltage is supplied to the lamp, it is supplied to the gap between the main and additional electrodes, which are located on one side of the quartz burner and to the same pair located on the other side of the burner. The second gap between which the mains voltage is concentrated is the distance between the main electrodes of the quartz burner, located on its opposite sides.
The distance between the main and additional electrodes is small, this makes it possible to easily ionize this gas gap when voltage is applied. The current in this section is necessarily limited by resistances located in the chain of additional electrodes before the entrance of the wire conductors into the quartz burner. After ionization has occurred at both ends of the quartz burner, it is gradually transferred to the gap between the main electrodes, thereby ensuring further combustion of the DRL lamp.
The maximum combustion of the DRL lamp occurs after about 7 minutes. This is due to the fact that in a cold state, the mercury in the quartz burner is in the form of droplets or deposits on the walls of the flask. After starting, the mercury slowly evaporates under the influence of temperature, gradually improving the quality of the discharge between the main electrodes. After all the mercury has turned into vapor (gas), the DRL lamp will reach its nominal operating mode and maximum light output. It should also be added that when the DRL lamp is turned off, it is impossible to turn it on again until the lamp has completely cooled down. This is one of the disadvantages of the llama, since it becomes dependent on the quality of the power supply.
The DRL lamp is quite sensitive to temperature and therefore its design includes an external glass bulb. It performs two functions: firstly, it serves as a barrier between the external environment and the quartz burner, preventing the burner from cooling (the nitrogen inside the flask prevents heat transfer), and secondly, since during the internal discharge not the entire visible spectrum is emitted (only ultraviolet and green color), then the phosphor lying in a thin layer on inside glass flask, converts ultraviolet light into a red spectrum. As a result of the combination of blue, green and red radiation, the white glow of the DRL lamp is formed.
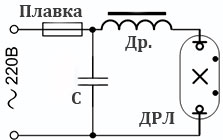 The four-electrode lamp is connected to the mains via a choke. The choke is selected in accordance with the power of the DRL lamp. The role of the inductor is to limit the current feeding the lamp. If you turn on a lamp without a choke, it will instantly burn out because too much electric current will pass through it. It is advisable to add a capacitor (not electrolytic) to the connection diagram. It will affect reactive power, and this will save electricity twice.
The four-electrode lamp is connected to the mains via a choke. The choke is selected in accordance with the power of the DRL lamp. The role of the inductor is to limit the current feeding the lamp. If you turn on a lamp without a choke, it will instantly burn out because too much electric current will pass through it. It is advisable to add a capacitor (not electrolytic) to the connection diagram. It will affect reactive power, and this will save electricity twice.
Choke DRL-125 (1.15A) = capacitor 12 uF. (not less than 250 V.)
Choke DRL-250 (2.13A) = capacitor 25 uF. (not less than 250 V.)
Choke DRL-400 (3.25A) = capacitor 32 uF. (not less than 250 V.)
P.S. The DRL lamp contains droplets of mercury inside; if the quartz flask breaks, the mercury vapor will disperse in a room of 25 square meters. Handle the DRL lamp with care.
Since DRL 250 high-pressure lamps have a fairly long service life and high efficiency compared to incandescent lamps, they are successfully used to illuminate summer cottages, the courtyard of a private house, and sometimes even indoor garages.
They have proven their reliability, quality of lighting over the years, and all this for a small amount of money. Purchasing a DRL 250 lamp will not be difficult. It is available for sale in both specialized stores and markets.

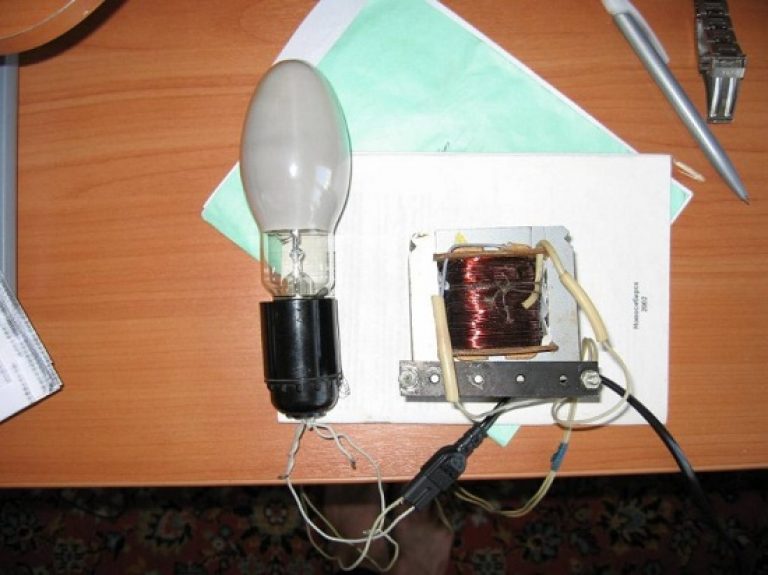
The problem may be the inductor, which is included in the lamp power circuit. Since it consists of copper wire, its cost, even used, is quite high. Therefore, this article will describe how to make a choke for this lamp from other commonly found materials. For example, from three chokes of once common fluorescent lamps. Such chokes were used in lamps for LD 40 lamps, respectively, their choke was 40 Watt. Also lamps for LD 80 lamps in which the chokes are designed for 80 watts. To replace the inductor for a 250-watt DRL lamp, you will need two 80-watt inductors and one 40-watt inductor. Schemes of their connection can be seen in the figure.
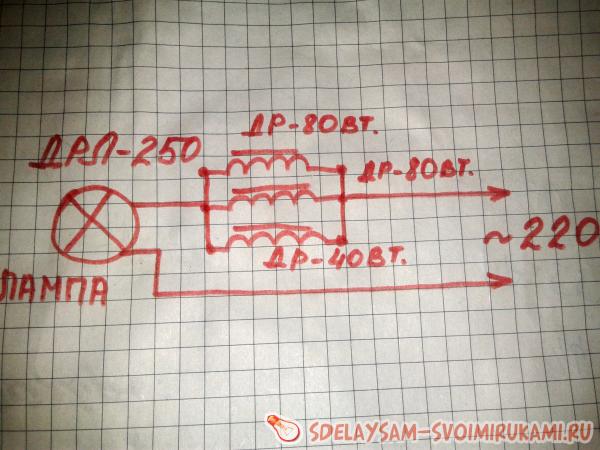
Here you can see that all the chokes are connected in parallel, that is, the chokes connected in parallel form one common ballast.
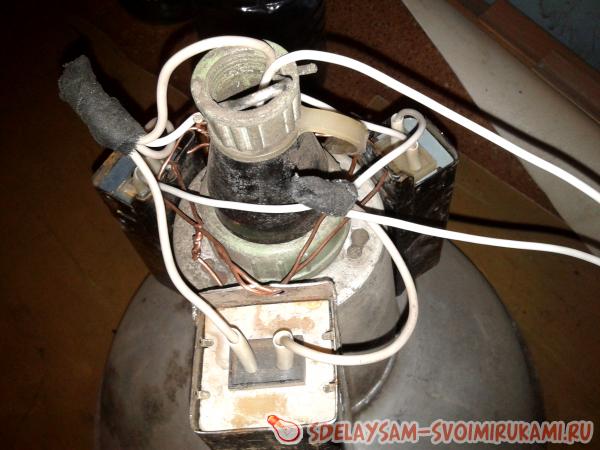
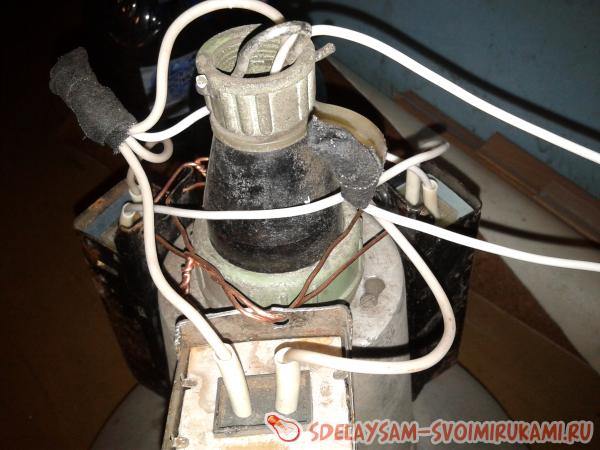


One wire coming from the 220 socket connects to one end of the chokes, and the other wire in the 220 socket goes directly to the lamp. The wire from the output of the chokes goes to the second contact of the lamp. An option for installing chokes on the lamp body can be seen in the photographs.
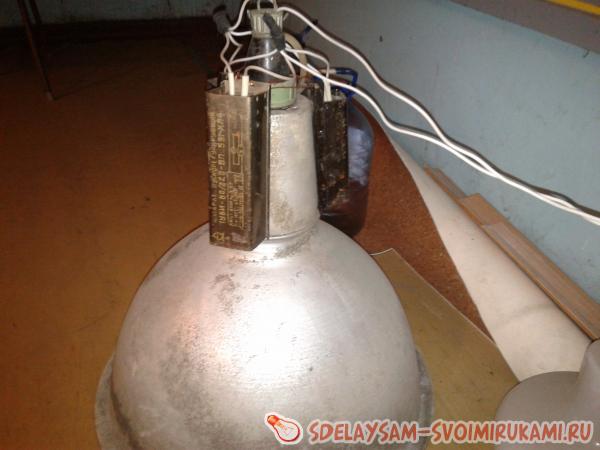

Here you can also see how the wires are connected. It is very important to ensure that the contacts on the inductor terminals have a good connection, otherwise they will spark and heat up. In the photo you can see how such a choke works and starts the DRL 250 lamp.
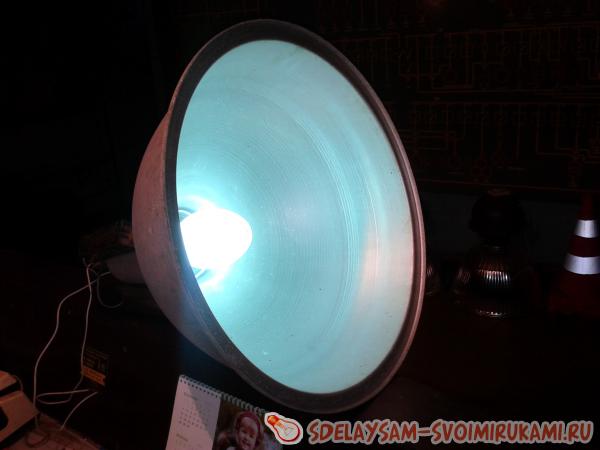

This design was made and tested, showing good results. In addition to installing chokes on lamps, you can make a separate box in which they will be located, and lead the wires from it to the lamp. This assembly option will cost much less than purchasing a special throttle. I would like to remind you that according to the rules for installing DRL lamps, they must be at a height of at least three meters. Since it is believed that they emit quite a lot of ultraviolet radiation, and this is undesirable for human skin.
That's all. Try it and you will succeed.
Many people have heard the word throttle. However, few people know what it means. What device is called a throttle? What does it look like? What functions does it perform?
Throttle usually invisible to humans. That is why few people know about its existence. And this despite the fact that currently none of the varieties of mercury lamps can work without it. A choke is a device that can rightfully be called the main part of ballasts installed in modern lighting devices.
From German the word throttle can be translated as limiter. This is its first task - to limit the amount of voltage that is supplied to the electrodes of the lamp when it is working. The second function is to create for a short period of time high voltage, which will be needed to turn on the lamp.
The principle of operation of the inductor is the process of short-term appearance of voltage in the coil at the moment an electric current passes through it. The values of current and voltage are carefully calculated and differ for certain models of these devices. These parameters help to penetrate the gaseous environment using a discharge of electrical energy. After turning on the lamp, the choke becomes a limiter. There is no longer any need for a working lamp great importance voltage. This feature made it more economical than other types of lamps.
Different lamps require different chokes. For example, a choke to a HPS lamp will not function with mercury lamps. This is due to the difference in the amount of current and voltage required to start, which ensures full operation of the lamp. But MGL lamps will work with both types of chokes. True, in each individual version the brightness and color temperature of the lamp will change.
An interesting fact is that the service life of the inductor is much longer than the service life of the lamp itself (if all operating rules are followed). Over time, the lamp gets old. As a result, the ballast begins to get very hot and even overheat. This leads to the system simply turning off or short-circuiting. Therefore, it is important to change them when their service life ends. To avoid problems, you can sometimes measure the voltage value in the lamp. This way you can avoid failure PRA, which costs much more than a lamp. Currently, lamps with a built-in automatic fuse are becoming increasingly popular.
According to their purpose, chokes are divided into several types. They can be single-phase or three-phase. They can work with 220V and 380V networks. Due to their design, which includes special protection, some types of chokes can work outdoors or in extreme conditions.
For long and high-quality operation of the throttle, it is important that it fully meets all the requirements stated for it.
Since DRL 250 high-pressure lamps are distinguished by their durability, reliability and high operating efficiency compared to standard incandescent lamps, they are often used to create lighting in summer cottages, courtyards of private houses, garages, etc. Such lamps themselves are quite easy to purchase in any specialized store, they have a very reasonable price and are very common. The problem is that the inductor that is included in the lamp power circuit consists of copper and can be much more expensive. Therefore, the author decided to try to make such a choke himself.
Materials and tools that the author used to create homemade chokes for the DRL 250 lamp:
1) 40 watt chokes from an LD 40 lamp
2) 80 watt chokes from LD 80 lamps
3) wires
4) blowtorch
5) soldering accessories
Let's take a closer look at the example of photographs on how to assemble a homemade choke for DRL 250 lamps.
As mentioned above, conventional chokes for a DRL 250 lamp are quite expensive, since they consist of copper wire. So he decided to make it himself from cheaper similar materials. As such materials, the author chose other chokes from less powerful fluorescent lamps.
Before using DRL 250 lamps, the author used LD 40 and LD 80 lamps, which have 40 and 80 Watt chokes, respectively. Therefore, it was decided to create a choke for DRL 250 from them. After making some calculations, the author found that for one DRL 250 choke, at least two chokes of 80 watts and one of 40 watts are needed.

Below is a diagram of their connection:
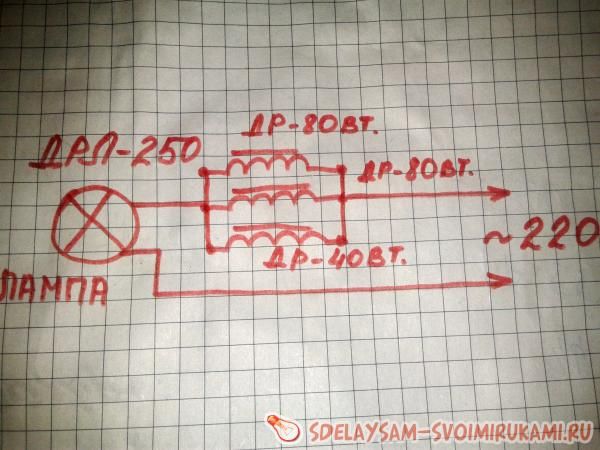
As can be seen from the diagrams, all chokes are connected in parallel, thus forming a common ballast. This is important, since when the chokes are connected in series, the inductance will add up and the inductive reactance will increase accordingly. Therefore, when connected in series, the current will be limited to the level of a 20-watt lamp.
The author connected one of the wires coming from a standard 220 V outlet to one of the ends of the inductor, and ran the other wire from the outlet directly to the lamp. The author connected the wire that comes from the output of the chokes to the second contact of the lamp. The practical application of such a scheme is presented in the photographs below:
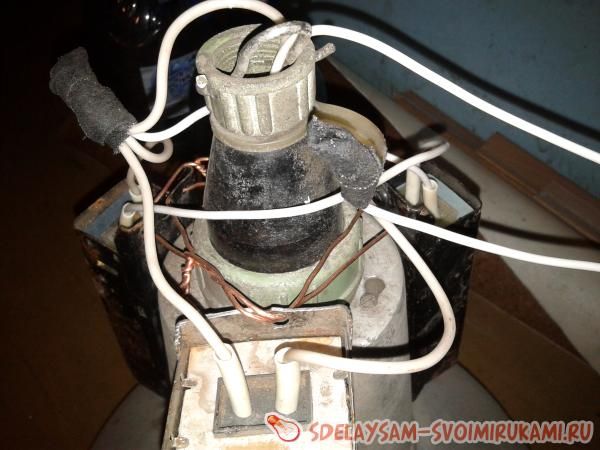
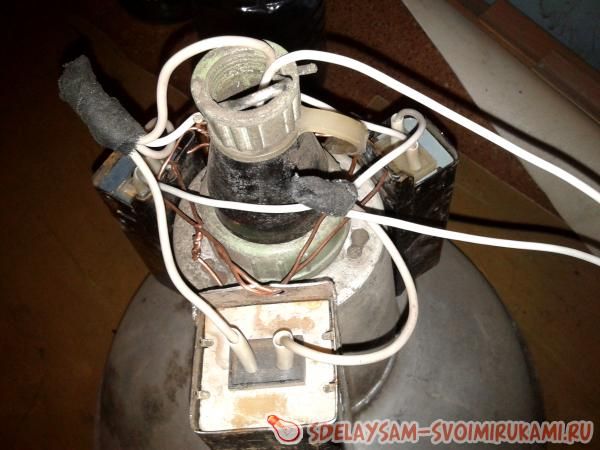
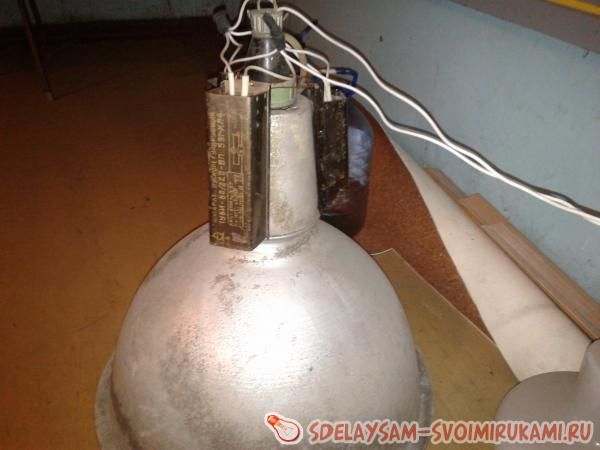



In these photographs you can also see exactly how the wires are connected. The author notes that it is necessary to ensure that the contacts at the inductor terminals have a fairly good connection, otherwise they will spark and heat up, which can lead to breakdown.
The following photo shows how such a choke works and that it is capable of starting a DRL 250 lamp:
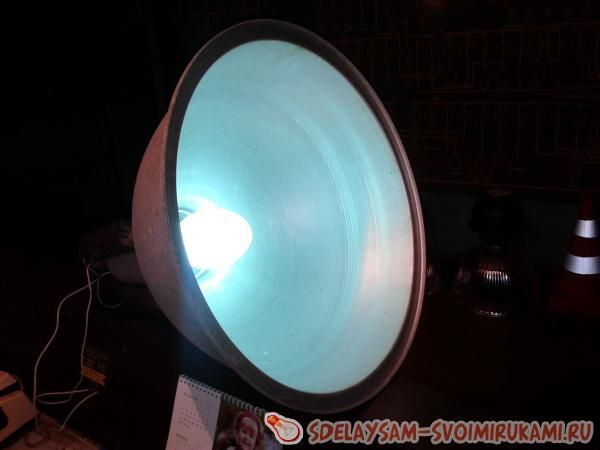

According to the author, such a scheme is reliable enough for use. So, in the future, he plans to use a separate box in which the chokes will be located, and simply lead the wires from it to the lamps. This assembly option cost the author less than buying a special choke for the DRL 250 lamp. The author also reminds that during testing special attention should be paid to safety precautions, and also advises placing the lamps at a height of at least three meters, since he believes that they are studying Quite a lot of ultraviolet light.
General purpose high-pressure mercury lamps (HPL) are intended for indoor and outdoor lighting fixtures, electrical networks with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220 volts.
To use them, appropriate ballasts are required.
1 Applications
The DRL lamp has high luminous efficiency, resistance to mains voltage fluctuations, low-cost ballasts that do not require pulsed ignition devices, and a long service life.
It is used to illuminate:
- streets;
- squares;
- industrial workshops;
- warehouses.
1.1 How do DRL lamps work?
Initially, DRL lamps had two electrodes. This required another triggering device - a high-voltage pulse test of the burner gap. The variety was discontinued and replaced with a 4-electrode version. To set fire, you need to connect the choke.
The main purpose of this element electrical diagram is a decrease over a certain period of time in the influence of range currents. A choke is a type of inductor.
For operation, alternating mains current is used. It is directed to the gap between the additional and main electrodes, which are located on one side of the burner to the same pair of electrodes, they are located on the other side of the quartz burner. The connected current is concentrated in the gap between the main electrodes of the burner; they are located on opposite sides.
The distance between the electrodes is quite small. Thanks to this gap, the gas is easy to ionize, by applying the required voltage to it. The current that occurs after a breakdown in the area is limited by electrical resistance. It is located in electrical circuit auxiliary electrodes that stand in front of the conductors entering the burner.
The discharge moves to the area between the electrodes of the quartz burner as soon as ionization begins at its ends. Next comes combustion.
The drl lamp reaches maximum combustion mode after 7 minutes. This happens due to the fact that unheated mercury is present in the form of deposits or droplets on the walls of the flask. After starting, the mercury lump evaporates under the influence of temperature, and the discharge between the working electrodes gradually improves.
After mercury turns into a gaseous state, the lamp reaches its nominal operating mode. It must be remembered that after turning off, it will not turn on again until the lamp has completely cooled down.
The lamp is very temperature sensitive, so it needs an outer glass bulb.
It has 2 functions:
- Serve as a barrier between the burner and the medium.
- Convert ultraviolet light into a red spectrum.
2 DRL lamp design
A DRL lamp has three main functional parts: a glass bulb, a quartz burner and a base. The outer part is a glass bulb. Inside it there is a quartz burner, to which conductors from the contact base are suitable. The air is pumped out of the flask and filled with nitrogen.

There are two limiting resistances in the bulb. The outer surface of the glass bulb is coated inside with phosphor and a drop of mercury.
2.1 Connection diagram for a mercury arc lamp
To connect the DRL lamp, you need to use special ballasts. These devices are different from those used to connect fluorescent lamps.
After switching on, a discharge occurs between the main and additional electrodes. The gas ionized in the burner ensures the ignition of this discharge between the main electrodes. After the lamp is ignited, the discharge between the auxiliary and main electrodes ends.
The choke, as a ballast device, limits the lamp current and stabilizes it if there are deviations in the network voltage.
Resistors will limit the current when the lamp is lit. The current at the moment of ignition exceeds the rated current by 2 - 2.6 times. As the burner heats up, the current decreases and the voltage increases from 65 to 130 V. Ignition lasts 5-10 minutes. The temperature of the outer flask in operating mode exceeds 200 degrees.
2.3 Luminaires with DRL lamps
For outdoor street lighting To make it comfortable and convenient at night, various lighting devices are used. Each of them differs in type, shape, power, light elements used, mounting methods and other characteristics. One of the most common— lamps etc.
Such lighting devices differ:
- power;
- brightness;
- durability;
- frost resistance;
- efficiency.
Two types of lamps are manufactured for DRL lamps, which best suit the area of use. Cantilever lamps are used for poles; they are mounted at an angle of 15 degrees relative to the horizontal. Designed for one or more lamps.

They have a built-in or external throttle. The reflectors and housing are made of special sheet steel. The lampshade has a protective glass cover or metal grille.
Floor lamps are made in the form of a transparent or frosted ball made of glass or polycarbonate. The base is a pillar, decorative pipe or support. Floor lamps with the shape of an inverted cone are also produced. The throttle is located inside the base of the lampshade. This is a decorative type of lamp, it is intended to decorate the lighting of the area.
The LPO fluorescent lamp, which has a simple design, is perfect for lighting various rooms. Such a lamp will be able to provide stable lighting over a wide voltage range.